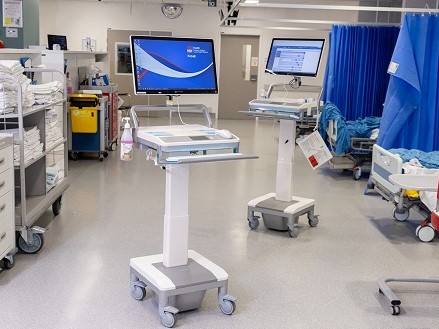
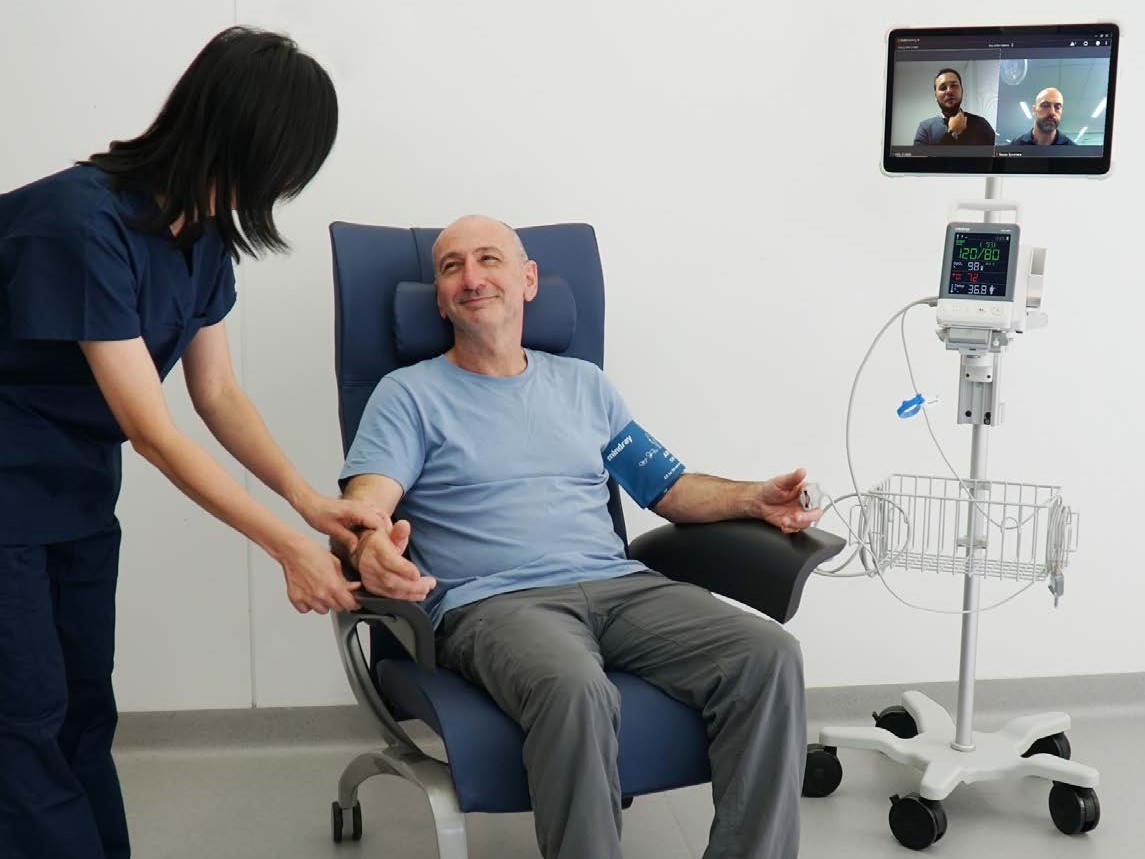
In hospital IT infrastructure projects, the focus is often placed on the software solutions and systems that power the medical operations and data management. While software plays a critical role in ensuring efficient workflows and seamless connectivity, it is important not to overlook the significance of End User Devices (EUD). These devices, including computers, tablets, smartphones, and other hardware components, are essential elements of a hospital’s IT infrastructure. They serve as the interface between healthcare professionals and the software systems, enabling effective communication, data input/output, and patient care delivery.
Here are 5 reasons why EUDs are just as important as the software itself in hospital IT infrastructure projects.
1. User Experience and Productivity
EUDs greatly influence the user experience of healthcare professionals. Devices with intuitive interfaces, responsive touchscreens, and ergonomic designs contribute to a positive user experience, allowing medical staff to navigate software applications efficiently. Seamless integration between software and hardware ensures that clinicians can easily access patient records, input data, and retrieve critical information, ultimately improving their productivity and enabling them to focus more on patient care.
2. Mobility and Point-of-Care Access
In a hospital environment, healthcare professionals need access to patient data and software applications at the point of care. EUDs, such as tablets or mobile devices, empower clinicians to carry their work with them, providing mobility and flexibility in delivering care. These devices allow doctors and nurses to view real-time patient information, update records, and communicate with colleagues, regardless of their location within the hospital. By reducing the need for manual data entry and facilitating quick access to relevant information, end user devices enhance workflow efficiency and enable timely decision-making.
3. Security and Privacy
In the healthcare sector, safeguarding patient data is of paramount importance. EUDs play a critical role in ensuring data security and privacy. These devices should be equipped with robust security features, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and remote data wipe capabilities, to protect sensitive patient information. Hospitals must also implement strict device management protocols to maintain control over the software applications and data stored on these devices. Neglecting the security aspects of end user devices can expose hospitals to data breaches, compromising patient confidentiality and potentially leading to legal consequences.
4. Integration and Interoperability
EUDs serve as the bridge between various software applications and systems within a hospital’s IT infrastructure. They need to be compatible with the software solutions used for electronic health records, laboratory management, pharmacy systems, and other healthcare applications. Seamless integration and interoperability between devices and software ensure that healthcare professionals can access a comprehensive view of patient information across different systems. This integration improves care coordination, reduces duplicate data entry, and enhances the accuracy and completeness of medical records.
5. Device Management and Maintenance
Hospital IT departments are responsible for managing and maintaining EUDs throughout their lifecycle. This includes tasks such as device provisioning, software updates, troubleshooting, and repairs. Well-managed devices contribute to the overall reliability and stability of the IT infrastructure. Proactive device management strategies, such as remote monitoring, asset tracking, and regular maintenance, ensure that devices are functioning optimally and minimise potential disruptions in clinical workflows.
While software systems are crucial for hospital IT infrastructure, end user devices play an equally significant role. They directly impact the user experience, productivity, mobility, security, integration, and overall effectiveness of healthcare operations. By investing in high-quality devices, hospitals can provide their staff with reliable tools that facilitate efficient workflows, secure data access, and seamless communication. Considering the importance of end user devices is essential for successful implementation and optimisation of hospital IT infrastructure projects, ultimately leading to improved patient care and outcomes.